The rim refers to the outer part of a vehicle wheel, usually consisting of spokes and a rim. The rim is a key component of automobile tires. It is mainly used to support the tire, bear the vehicle’s weight, transmit driving and braking forces, etc. The structure and performance of the rim have an important impact on the car’s performance, safety, and driving mileage. There are many types of rims based on different classification standards.
♦Cast rims
Rims of various shapes and sizes are manufactured by melting metal and pouring it into molds to cool and shape. Cast rims have the advantages of low cost and high production efficiency, and are widely used in the fields of commercial vehicles and construction machinery.
Casting is divided into two types: gravity casting and low-pressure casting.
Gravity casting involves pouring liquid alloy into a mold to cool and form. Because the manufacturing process is simple and the molding is durable, it has become the lowest-cost manufacturing method.
Low-pressure casting uses low pressure to press liquid alloy into the mold so that the metal molecules are evenly distributed and can create more complex and delicate shapes.


♦Forged rims
rims of different shapes and sizes are manufactured by heating a metal blank to a high temperature and then forging it. The entire rim requires less material to achieve sufficient stiffness, and the overall weight is lighter. Forged rims have the advantages of high strength, light weight, good heat dissipation, higher safety, and strong plasticity. They are often used in high-end cars and sports cars.


♦Cast iron rims
Cast iron rims are generally used on medium-sized trucks. They are characterized by low cost but poor heat dissipation
♦Aluminum alloy rims
Made of aluminum alloy materials, aluminum alloy rims are widely used in cars and motorcycles. It has the advantages of light weight, good heat dissipation, and elegant appearance.
♦Steel Rims
Steel rims are commonly found on some of the more durable construction vehicles and trucks because of their high strength and load-bearing capacity.
♦Carbon fiber rims
Commonly used in high-performance cars and racing cars, carbon fiber rims are lighter and offer superior strength, but are relatively costly.
♦Deep groove rim
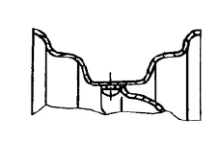
This kind of rim is integral and has a deep groove in the middle of its section. Mainly used in cars and light off-road vehicles. It has a shouldered, raised edge that holds the tire bead. Its shoulders are usually slightly tilted toward the middle, and their tilt angle is generally 4 to 6 degrees. The maximum diameter of the inclined part is called the diameter of the tire bead and the rim. The middle part of the cross-section has a deep groove shape to facilitate the disassembly and assembly of the tire. Deep groove rims have a simple structure, high stiffness and low mass, and are more suitable for use with small-sized tires with greater elasticity. Larger and stiffer tires are difficult to fit into such a one-piece rim.
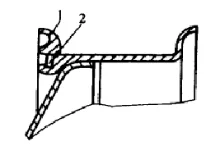
♦Flat bottom rim
There are many structural forms of this rim. As shown in the figure, the retaining ring 1 is integral, and an open elastic locking ring 2 is used to prevent the retaining ring from coming out. When installing the tire, first put the tire on the rim, then put on the retaining ring, and push it toward the middle until the tire crosses the annular groove on the rim, and then insert the open elastic locking ring into the annular groove.
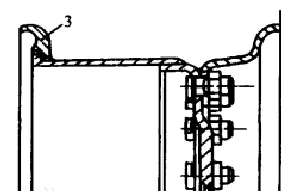
♦Split rims
This kind of rim is composed of inner and outer parts. The width of the inner and outer rims can be equal or unequal, and the two parts are connected together with bolts. When disassembling the tire, simply remove the nut. As shown in the figure, the retaining ring 3 is detachable. Some rims do not require a retaining ring. Instead, the rim is integrated with the inner rim to play the role of a retaining ring, and the inner rim and the spoke plate are welded together.